Author: John Li, Technology Analyst at IDTechEx
Autonomous emergency braking (AEB) is one of the most important ADAS (advanced driver assistance systems) features a vehicle can have. Studies have shown that pedestrian crash risk is reduced by 25-27% and pedestrian injury crash risk by 29-30% through the implementation of AEB. As discussed in IDTechEx’s new report, “Infrared (IR) Cameras for Automotive 2025-2035: Technologies, Opportunities, Forecasts”, LWIR (long-wave infrared) camera technologies could drive the improvement of AEB systems in darkness and adverse weather conditions. IDTechEx assesses existing regional regulations on AEB and the effect they will have on the adoption of infrared camera technologies in ADAS.
The US passenger vehicle market will be the first to adopt LWIR cameras due to NHTSA’s US regulations
The first and most important regulation to be aware of is NHTSA’s ruling for AEB and pedestrian AEB in the US. In its report, NHTSA details the progress made in vehicle safety due to AEB, before setting a 2029 deadline for all new vehicles installed to have AEB with more stringent requirements. A key requirement is that all new vehicles pass automatic braking tests against lead vehicles and pedestrians using a minimum level of illumination (low-beam headlights) with ambient lighting of 0.2 lux (night), as over 75% of pedestrian injuries occur in non-daylight conditions.
NHTSA believes that only 5% of new vehicles by 2029 will require hardware upgrades to meet these demands, as most vehicles will have advanced camera and radar technologies by 2029, such that only software upgrades are required. However, the more pessimistic response from automotive OEMs and tier-one suppliers is a suggestion that this is potentially optimistic.
While current AEB systems use a combination of camera and radar technologies, both SWIR (short-wave infrared) and LWIR technologies would provide an additional sensing mode that is unaffected by darkness or fog. IDTechEx predicts that some OEMs will turn to these technologies to meet NHTSA’s requirements, while others will upgrade existing camera and radar hardware, or may install additional hardware such as LiDAR. Further details, analysis, and forecasts are discussed in IDTechEx’s new report, “Infrared (IR) Cameras for Automotive 2025-2035: Technologies, Opportunities, Forecasts”.
Opportunities and regulations in Europe, China, and other regions
While regulations in other regions haven’t been as explicit yet, there are targets regarding AEB and vehicle safety overall, which may have an impact on the uptake of AEB in vehicles. In the EU, all new vehicles were mandated to have AEB systems installed in 2022, and this was extended to existing vehicle models in 2024. On top of this, the EU’s Vision Zero initiative aims to achieve zero road fatalities by 2050, with an intermediary goal of halving the 19,800 fatalities in 2021 by 2030. This included a ~US$7.6 million project, PROSPECT, which investigated camera, radar, and LiDAR technologies for pedestrian detection and AEB.
In 2023, the number of road fatalities in the EU was approximately 20,400, only a 1% decrease compared to the number of road fatalities in 2022. This includes countries such as Spain, France, and Italy, where fatalities have barely decreased since 2019, and Belgium, Hungary, Poland, and others, where the number has increased. Combined with Europe-centric projects such as the HELIAUS Project and the lack of progress in reducing pedestrian fatalities, IDTechEx expects the technology developments driven by NHTSA’s regulation to also be adopted in Europe from 2027, although this will be more gradual due to the lack of concrete regulation.
The market penetration of AEB in China lags behind Europe and the US overall. IDTechEx estimates that the market penetration of AEB in the Chinese passenger market is approximately 40% as of 2024. In terms of sheer volume, however, China sold 30.1 million passenger vehicles in 2023, compared to 10.5 million in Europe in the same year. Combined with the projected increase in AEB penetration to exceed 60% by 2030, China presents a market opportunity for LWIR thermal cameras over the next 10 years. As is expected in Europe, the technology developed in anticipation of the US market will result in a rise in LWIR-fused AEB in the Chinese market, starting from 2027.
The three largest passenger vehicle markets (the US, Europe, and China) all have their own New Car Assessment Programs (NCAP). These are evaluations of a passenger vehicle’s overall safety using standardized test conditions. In the US, these are operated by NHTSA and are mandatory for every new vehicle, including its new night-time AEB condition tests, to be carried out in 2029. The Euro NCAP, in contrast, is voluntary but has its own tests for vehicle and VRU (child/adult pedestrian, cyclist, motorcyclist) encounters. At the start of 2024, China’s new C-NCAP regulations replaced the previous version from 2021 and placed greater importance on ADAS features such as AEB and VRU detection.
The C-NCAP involves AEB tests with pedestrians and two-wheelers, with speeds ranging from 10-80 km/h. It also covers scenarios where pedestrians are hidden from view or when a vehicle is making left and right turns. IDTechEx is aware of two Chinese OEMs introducing LWIR night vision into their vehicles. The technology is on the roads from these OEMs, and also OEMs such as General Motors, BMW, and Mercedes, which have historically had optional night-vision systems. Hardware and software upgrades would be required to integrate LWIR sensing into AEB for ADAS, but the fact that the technology is already being used reinforces IDTechEx’s forecast for LWIR-integrated AEB to enter the Chinese market at a similar time and rate to in Europe. Other regions, including Japan and India, have their own NCAP-style tests for assessing the overall safety of vehicles.
Autonomous driving and IDTechEx outlook
AEB will encourage the adoption of LWIR cameras in SAE level 1-3 vehicles, with most current on-road vehicles being level 1 or 2 in the European, US, and Chinese markets. IDTechEx predicts that there will be an even larger demand for LWIR cameras for autonomous driving when SAE level 4 vehicles and robotaxis enter regional markets in the long term. With greater demands on sensing for human-less driving put on thermal sensors, this is where higher definition cameras, as well as upgraded software and stereo vision technologies, would be required of LWIR cameras. From the early 2030s, IDTechEx expects autonomous driving in SAE level 4 vehicles and robotaxis to be the dominant driver to further LWIR camera adoption in passenger vehicles. Granular forecasts by region and SAE level can be found in IDTechEx’s new report, “Infrared (IR) Cameras for Automotive 2025-2035: Technologies, Opportunities, Forecasts”.
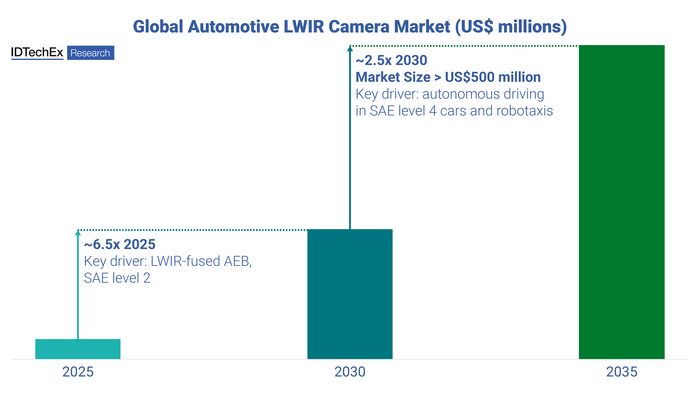
IDTechEx expects the initial uptake of automotive LWIR cameras to increase the yearly market size by 6.5 times between 2025 and 2030, driven primarily by NHTSA’s regulations, as well as updated regional NCAP testing programs and safety initiatives. IDTechEx expects SAE level 4 vehicles and robotaxis to enter the market at the start of the 2030s. This will further drive automotive LWIR camera adoption, increasing the market by 2.5 times from 2030 to 2035. LWIR cameras for autonomous driving will require higher resolutions and possibly more per vehicle, compared to LWIR cameras for AEB. Source: IDTechEx – “Infrared (IR) Cameras for Automotive 2025-2035: Technologies, Opportunities, Forecasts”
To find out more about this new IDTechEx report, including downloadable sample pages, please see www.IDTechEx.com/InfraAuto.
For the full portfolio of sensors market research available from IDTechEx, please visit www.IDTechEx.com/Research/Sensors.

