1. Introducing data science to business practices in a wide range of fields. Murata's data science initiatives
At Murata, the Data & Analytics Department plays a central role in solving problems through data science.
These initiatives are not limited to manufacturing, design, and development at our own plants but are also being put into practical use in marketing including sales and the web, as well as IoT devices, healthcare, and other new businesses.
Examples of initiatives in various fields together with comments from the persons in charge are introduced below.
Manufacturing site initiatives
We are collaborating with manufacturing sites to apply data science operations to improve operational efficiency and solve problems at such sites.
Data science is being applied to automate the proposal of optimal production plans in our plants utilizing big data accumulated in-house and to automate the detection of product characteristic anomalies within inspection processes where lack of uniformity in human inspection results was a problem.
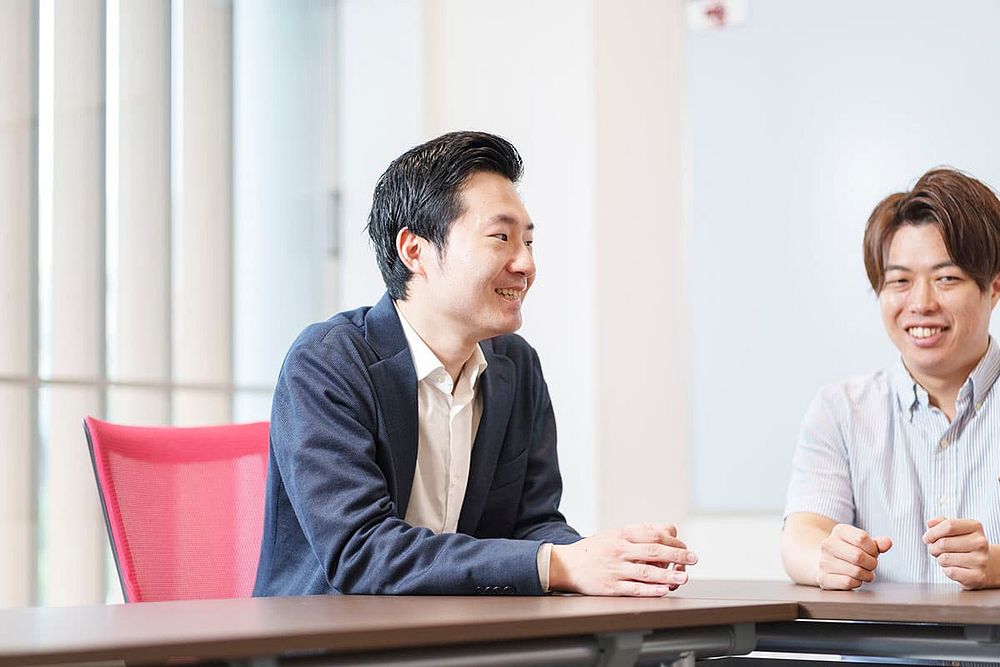
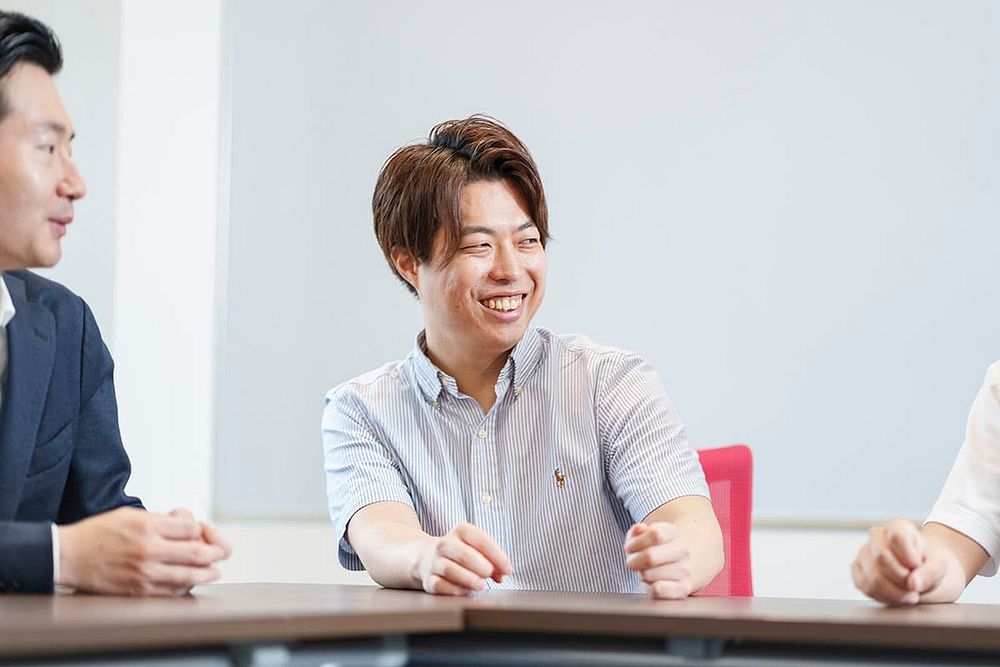
Higashi: “In my previous job, I worked on data science in the manufacturing industry. What I found attractive about Murata was the richness of data. We manufacture hundreds of millions of products at our plants every day, and I don't think that there are many environments that can handle data at such a large scale. At the manufacturing sites, it is important to know what kind of data is being collected and how it is collected. On that point, Murata has long had a culture of actively collecting data to perform statistical analysis. This enables close collaboration with the manufacturing sites from the stage of collecting data to identify and solve problems. We can quickly apply data science to solve problems and improve operational efficiency.”

Higashi discusses the application of data science at manufacturing sites
Sales and marketing initiatives
We internally released a web access analysis tool for marketing managers. This tool can extract latent customer needs from web access data with AI to propose the optimal products.
In addition, we developed and introduced an AI system that assigns response requests to the most suitable department based on the content of a customer's inquiry. This successfully shortens customer response times and helps improve customer satisfaction.
All of these internal products were developed by the Data & Analytics Department.
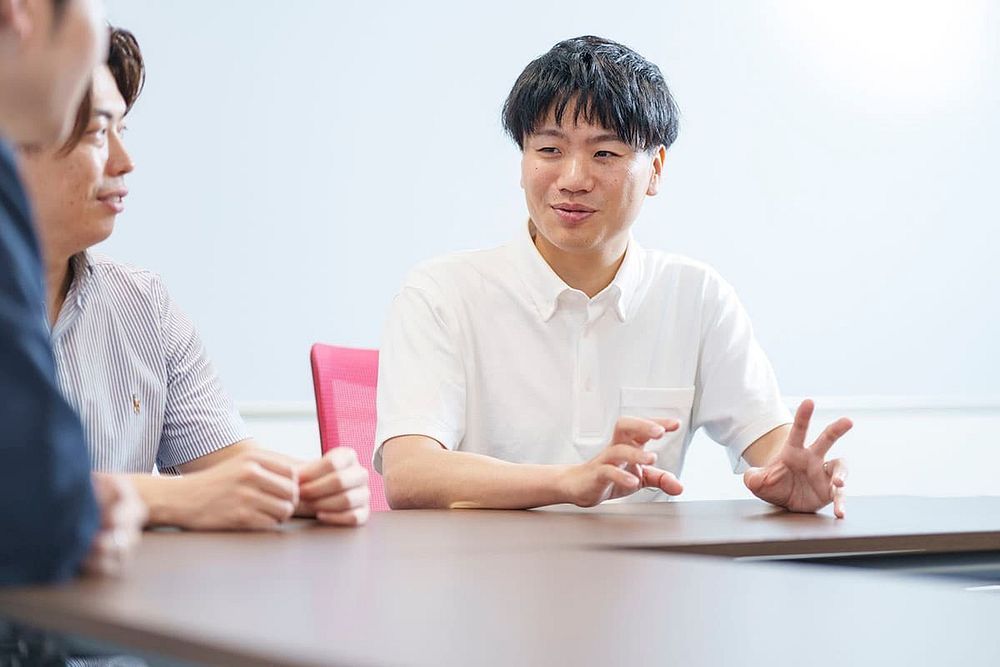
Nakano: “People who come to Murata as interns are surprised to learn that we are applying data science to the fields of sales and marketing. When I changed jobs to work here, I was similarly surprised by what I found, as I had a strong conception of Murata as a manufacturing company. In my previous job, my work as a system integrator was centered around what the customers wanted. However, at Murata I can come up with my own ideas and immediately apply them, which is very appealing. In my work, I identify needs and problems by interacting with people in the field and use data science to provide insights that will assist with decision-making and streamline tasks.”

Nakano discusses the application of data science to sales and marketing
New business initiatives
In addition to electronic components, Murata also develops, manufactures, and sells technology-enabled hardware products, associated software, and services. For example, in applications that detect anomalies in equipment using vibration sensors and new businesses related to healthcare, data acquisition and analysis as well as the construction of AI models are essential to improving performance.
What data should be acquired concurrently with product development and how should it be processed to achieve results? We examine the added value of the business from both hardware and software perspectives.
Matsui: “I was also a system integrator in my previous job and handled customer data to a limited extent, so project execution took a certain amount of time. However, at Murata I can work in collaboration with the hardware design and development department to consider the data to be used and tackle new businesses with a sense of speed. For example, when it comes to the question of what kinds of signals to acquire from our own sensors, I think that the ability to produce my own ideas and obtain the opinions of those around me is unique to Murata, which manufactures hardware and creates algorithms in-house.”

Matsui discusses the application of data science to new businesse
2. Advancing projects through internal and external collaboration
At Murata, the Data & Analytics Department does not carry out various initiatives on its own. In order to expedite projects, cross-sectional collaboration without barriers is the key to making practical application a success.
Collaborating internally on data science
At Murata, professionals from various fields such as the manufacturing of numerous products, development of new products, sales and marketing, and services, etc. engage in a close exchange of opinions with the Data & Analytics Department to promote and accelerate the implementation of data science in each operation.

Higashi: “There are many things that cannot be understood just by looking at the data. In that regard, because we are using data science internally, we are able to speak directly with the people who are performing data maintenance on the relevant equipment at the manufacturing sites. In this frank and straightforward communication within the company, there are many insights that cannot be gained through numbers alone. I always feel that close collaboration with the people who are facing problems is very important to solving problems and realizing efficiency in data science.”
Nakano: “I use various approaches in my work such as listening to problems from people in the field and solving them with data science or creating project proposals myself. Initiative is also respected within the departments, so I think that the percentage of project proposals created by us will increase in the future. At Murata, you can drive projects with a sense of speed while producing ideas, so it might be a very satisfying workplace for those who aspire to become consultants, for example.”
Collaborating externally on data science
In new businesses, we actively create new forms of value in new products and services that use data science by collaborating with external professionals at medical institutions and other fields as needed.

Matsui: “In new businesses related to medical instruments, we conducted joint research with medical institutions. Physicians helped us consider what kinds of data to acquire, and we were able to proceed with the research while receiving various forms of feedback. I think that having the opportunity to work together with external experts such as physicians is rare even in the field of data science.”
3. A strong organization that cultivates the ability to put ideas into practice
The Data & Analytics Department is not a transient organization that is riding the recent booms in DX and AI. As a group of data science experts within the company, we are constantly learning the latest technologies while developing AI models and building systems to put them into practical use.
Within the company, we also have people from national research institutions and specialists with PhDs. There is an atmosphere in which the people involved actively share their skills and knowledge to mutually improve one another.
In addition, we also host events such as hackathons and in-house Kaggles to create new ideas and cultivate the ability to put those ideas into practice.
Matsui: “At hackathons held in the past, we would create a problem, think of a solution, consider how to achieve it, and implement it (create a demo app) in one or two days. In addition, we also hold Kaggles, which are internal events in which the participants use every available technology to compete with each other based on the precision of the machine learning models that they each create to improve our technical abilities and exchange technologies within the company.”
Furthermore, we are engaging not only in company-wide and departmental training but also multilayered initiatives that will lead to a deeper understanding of data science. Several examples are introduced below.
Post-employment training and catching up with the latest technologies
There is a set of guidelines for new employees called “Technical Onboarding” for efficiently learning required knowledge such as statistics, deep learning, etc. In addition, it is also part of the work of employees, including current employees, to learn and share the latest technologies that are advancing day by day. In the Data & Analytics Department, we use about 20% of our time for continuous skill acquisition, and it can be said that there is a culture of respect for skill development through learning.
Matsui: “New graduates, experienced mid-career hires, and naturally current team members as well must continue to learn about the latest technologies and information. In order to continue catching up with the latest technologies and information, the staffers inside departments are always introducing new research papers and useful technical books to one another. Furthermore, you can learn a lot by actively participating in conferences, so I find it to be a fascinating activity.”
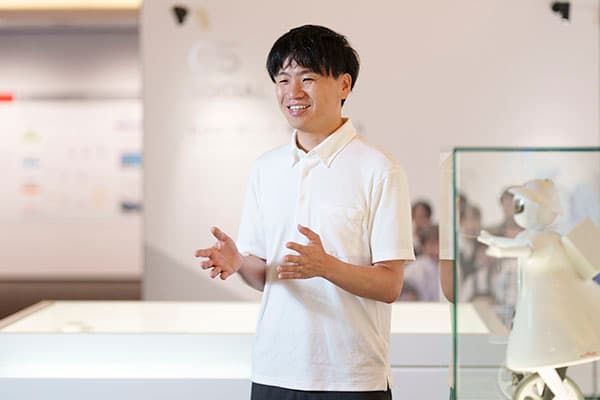

Nakano: “Because I was a system integrator in my previous job, I had more work experience in engineering than data science. After joining Murata, the senior colleague who was in charge of my data science OJT offered personal guidance and told me, 'It is the job of a data scientist to understand the theory behind advanced analysis methods,' and I was able to master the skills. Later, I was placed in charge of OJT for new employees, and now in their second year they are developing AI models for actual projects, building systems that embed those models, and implementing them on their own.”
In-person data science support at each site
Each office and plant is also deepening their understanding and skills in utilizing data, and there are also efforts to raise the level of data science across Murata. As part of efforts to support the improvement of problem-solving skills using data science being promoted across the company, the Data & Analytics Department is providing in-person training support.
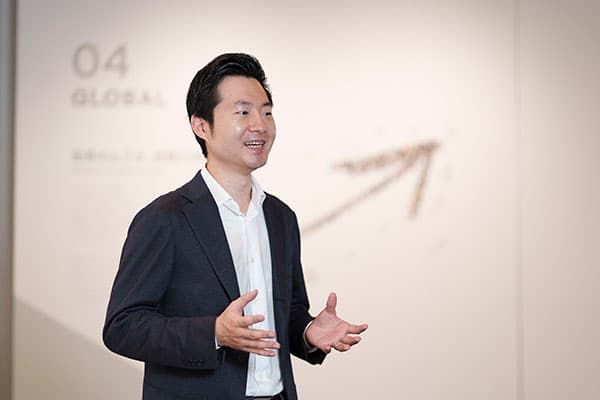
Higashi: “I personally went to our own plants to provide in-person support. This activity supports the participants, from defining problems to presenting solutions using data science. On the day of the presentation, the employee cafeteria served a special menu, etc. to create an event-like atmosphere. There is an interest in data science and a mood of excitement about this initiative across the company.”

Planning and implementation of voluntary study sessions
In the Data & Analytics Department, team members create ideas in a bottom-up fashion and can execute them with a certain degree of discretion. Study sessions are planned and implemented as part of those efforts.
Nakano: “The members of the Data & Analytics Department are required to drive the projects that they are in charge of with a sense of ownership. At the same time, the culture also values voluntary challenges. When I changed jobs and joined the company, I was a little bit confused at first, but I gradually became used to how things are done at Murata. For example, I recently hit it off with someone that I met in training and we ended up planning and holding an AI idea review meeting*1 in the manufacturing department of a certain product. Requests to hold similar meetings from product departments and the manufacturing departments of other products subsequently increased, and it is now developing into a significant activity for us.”
*1 The AI idea review meetings start with an introduction of 11 carefully selected data science techniques. The participants brainstorm and then select from 11 solution cards to identify problems in the field and solution techniques to link them together. This linking process enables the participants to simultaneously learn about data science techniques and generate ideas.

The “building of a strong organization” with abundant human resources, training, and challenging opportunities is an active investment in the data science field, which will be essential going forward, while supporting Murata's high market share in electronic components.
At the same time, it can be said that improving data science techniques and accumulating know-how are creating a virtuous cycle in which they are being applied to enhance and streamline, etc. product manufacturing, inspection, development, supply, and services.
4. Accelerating data science in an environment of abundant data and hardware
Murata develops and manufactures various types of hardware such as electronic components, sensors, modules, etc. while also enabling an environment where employees can engage in data science using diverse and vast sources of data.
This makes it possible for employees to solve hardware problems with data science and propose ideas for data utilization with hardware. In this way, the ability to rapidly approach problems from both hardware and data can be described as a key feature of the environment for conducting data science at Murata.

*The information in this article is current as of the date of publication. Organization names, etc. may be subject to change.